 *By César Ripari
*By César Ripari
Data is now widely recognized as an organization's greatest assets, fundamental to supporting smarter decisions. However, it is clear that many companies still act in a disorderly way with them, without an effective strategy. Those who seek to establish it face numerous challenges. Simply continuing to work without it being defined is no longer a viable option. It is essential to have a strategy, and, based on it, create a structured plan to define how to manage, use and extract value from data, covering policies, processes and technologies to guarantee the quality, security and compliance of information.
Like a true map, data strategy helps promote a data-driven culture and initiatives aligned with general and specific business objectives. The preparation of this plan requires special attention to highly relevant factors that will help companies avoid deviations, inconsistencies and inappropriate use of information. To prepare an efficient plan, we can highlight the main steps that every organization must follow:
- Align organizational goals: The goals of the organization's entire data strategy must be aligned. Collaboration between departments is necessary to define the data use strategy, specific processes and areas in which information can play an important role in achieving the organization's goals.
- Assess the current situation: It is important to carry out a comprehensive analysis of current data assets, processes and skills, organizing an inventory of data sets by business unit, identifying their appropriate sources and quality. It is also necessary to evaluate the technological infrastructure for storage, processing and integration to identify adjustment needs. The information governance methodology must also be validated to align roles, responsibilities and compliance.
- Identify use cases: Involve key stakeholders from the company's various departments to collect insights and discover what they are looking for in relation to data. At this point, it is important to assess: what are the main business objectives of each sector; what types of data are essential for daily operations and decision making; how data is managed and used, in addition to the main challenges (or concerns) related to data that are currently faced.
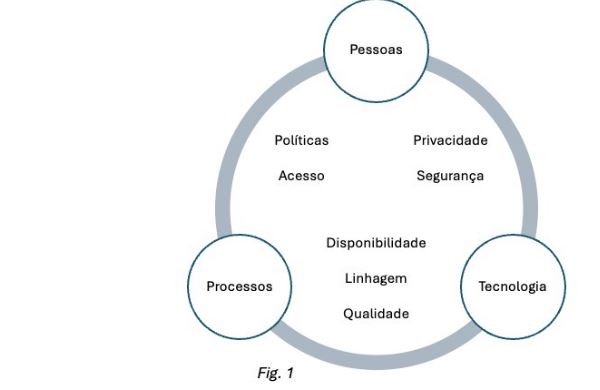
- Develop the data governance framework: Prepare the environment for a balanced implementation of solid governance measures, considering People, Processes and Technologies as a basis (fig. 1). Still at this stage, define the fundamental elements of the framework, including roles, responsibilities and policies. All principles and objectives for adopting the measures must be outlined at this stage.
- Define data architecture: Data engineers must design a scalable and flexible architecture, aligned with the business and taking into account the growth in the volume of information and technological advances. AND It is important to develop a data model and integration strategies for a seamless flow between systems.
- Establish data quality standards: Define a data quality process, metrics and standards to ensure accuracy and consistency in analysis. Involve key players stakeholders in the data quality cycle (fig. two) for validations and limits on the use of information and expectations regarding the information.

- Establish security and privacy measures: Identify security and privacy requirements, establish protection measures for sensitive data, possible vulnerabilities and security threats. Pay attention to current regulations and ensure alignment with internal policies and procedures. Establish regular security audits and assessments to help identify and act on proactively address possible weaknesses found.
- Define processes for the data lifecycle: It is important to define clear processes at all stages of the “life” of data: from collection, storage, processing to data disposal, with ethical and governed guidelines. Among these steps, all processes must be mapped in detail, including data origins, usage profiles, transformation and integration, migration between environments and systems, retention and archiving, backup and recovery, access controls, supervision and governance, and constant monitoring of data quality.
- Define strategies for Analytics and Business Intelligence (BI): Develop strategies to leverage all of the organization's data into IT solutions Analytics and Business Intelligence. Identify KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) and defining corporate metrics aligned with the organization's objectives are important factors for data-based decision making.
- Develop data literacy initiatives: Plan educational programs to promote a conscious environment regarding reading, understanding and communicating through data. Identify target audiences and their specific training needs in the use of data, including soft skills. Well-defined communication must be established, supported by management levels and the importance of data in decision-making must be emphasized.
By following these 10 steps, companies can establish a solid foundation for an effective data strategy. However, it is important to emphasize that it should not be seen as a static project, but rather a continuous process of improvement and adaptation. Reviews and adjustments must be made as business needs evolve and new technologies emerge. This way, organizations can remain at the forefront of innovation, leveraging the full potential of data to drive business evolution.
*César Ripari is Leader of the BI and Analytics Committee of the Brazilian Association of Software Companies (ABES) and Director of Pre-Sales for Latin America at Qlik.
Notice: The opinion presented in this article is the responsibility of its author and not of ABES - Brazilian Association of Software Companies














